Affinities & Differences
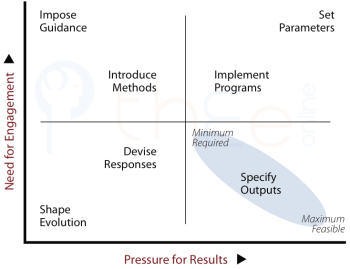
that share a TET-quadrant have a natural affinity, while those in diagonally opposite quadrants reveal a contrast. Although the contrasting qualities complement each other, personal identification with a method may result in conflict or dissatisfaction in practice.
Affinities within Quadrants
The most obvious affinities are between the two within quadrants.
Each quadrant contains a more extreme and a less extreme method, with two versions of the in the lower right. This is shown in the diagram via arrows; and it allows two circles to be drawn containing two contrasting sets.
The outer circle are evidently contextual and strategic in nature. The manager stays largely above and away from the mechanics of work. This corresponds to the conceptual construction of reality.
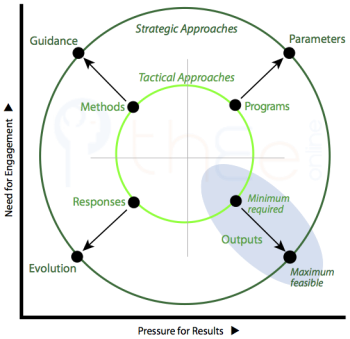
The inner circle are about activities and details of work processes related to the desired results. The manager here is necessarily immersed in practicalities of various sorts. This corresponds to the use of information to construe reality.
Within each quadrant, the inner method looks to its related outer method for facilitation and direction:
- that handle emerging issues look primarily to how the overall situation is being to facilitate and justify expedient choices.
- look primarily to to determine priorities for addressing the efficiency and effectiveness of work processes.
- are implemented on the basis of within their terms of reference.
- are developed based on judgements of what is optimum and believed .
Approach Duality
The 7 are also located along two diagonals of the TET. The diagonals define the approach duality and identify two contrasting sets of methods.
Managing via Activation

One diagonal from bottom left to top right includes a set of methods that can be labeled activating. These intrinsically stimulate activity and have the potential to generate progress directly.
In moving up the diagonal, the methods increasingly as follows:
- : these interventions are subtle because the aim is to go with the flow and build on what exists.
- : the crisis or disruption must be directly addressed, often urgently and often in relation to a hidden cause or a suppressed issue.
- Implementing programs: managing brings people together to cooperate and collaborate in a systematic fashion.
- Setting parameters: the provision of mandates and boundaries liberates imaginative possibilities.
Managing via Constraint
The other diagonal from bottom right to top left includes a set of methods that can be labeled constraining. These intrinsically interfere with what you and others might naturally do or prefer—for the benefit of the work itself.
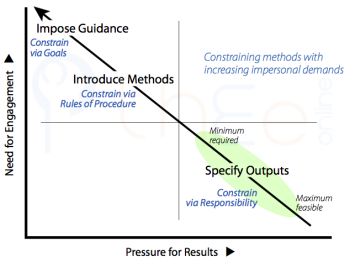
In moving up the diagonal, the methods make as follows:
- : these interventions depend on you accepting responsibility (and often accompanying accountability) for the outputs, and then allowing that inner responsibility (and external accountability) to govern the way you manage their work.
- : here you and all others involved are brought to agree to procedural rules in regard to tangible work processes so as to enable greater efficiency, ensure legal compliance or generate some other system benefit.
- : the values and objectives that are insisted upon serve as the ultimate justification for all work and are expected to constrain all your choices and subsidiary goals.
-
Explore additional features of the diagonals and quadrants.
then
- Consider how all the methods might combine.
Originally posted: 27-Nov-2013